When You Smoke Marijuana, This Is What Happens To Your Body

Some call it weed, pot, and many other names, and despite its popularity in the late XX century, this crop has been cultivated by people for several millennia.
According to a study of ancient pollen, the plant evolved from the Tibetan Plateau.
These days, it has gained a towering and often controversial reputation as a medicinal, recreational, and spiritual product. Marijuana has very diverse meanings in various cultures.
In most cases, people roll it up into “joints” and smoke it like cigarettes. Others put it in pipes, while some turn it into “edibles.”
Recently, cannabis has been decriminalized and legalized in many jurisdictions. As a result, more people are comfortable with its use.
Additionally, this has given scientists more freedom to research the drug and its effects.
Marijuana is unique in that it can be described as a depressant, hallucinogen, and stimulant at the same time.
The main ingredient in marijuana is Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is its primary psychoactive chemical. Marijuana has many strains, each of which has its concentration of this compound.
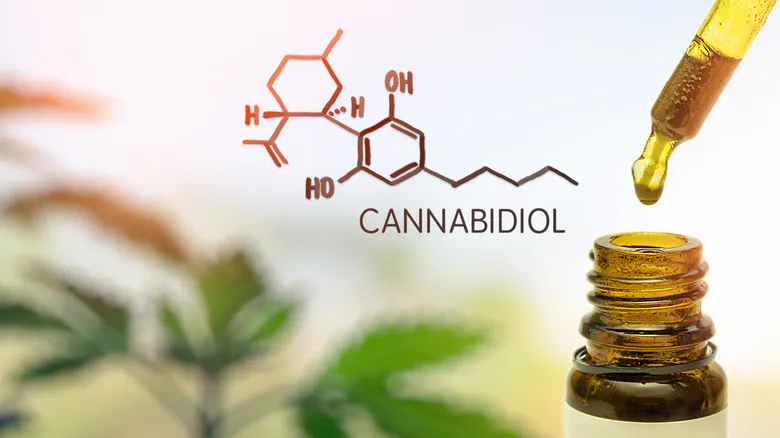
Marijuana also contains CBD, or cannabidiol, which can boost health without psychoactive properties.
For the most part, the effects of using marijuana are pretty predictable. The more exciting effects include having a philosophical outlook on life, some level of paranoia, the ability to forget life’s troubles, and so forth.
That said, the effects of consuming marijuana can take other forms depending on the person, the strain they have taken, and the circumstances. While some people can calm down after taking marijuana, others can go into a panic.
Here are some of the things that happen to your body when you smoke marijuana.
1. Feelings Of Euphoria

THC causes the high that comes with consuming marijuana. After smoking marijuana, this chemical gets into the bloodstream through the lungs and gets into the brain.
Once this compound gets into the brain, it affects the endocannabinoid system. It does this by imitating anandamide, which is a cannabinoid found naturally in the body.
The THC results in messages being sent throughout the body’s nervous system.
Anandamide comes from the Sanskrit word “ananda,” which means “bliss.” You get this feeling after running or eating chocolate.
Anyway, once you smoke weed and the THC gets into your brain’s cannabinoid receptors, it can cause emotions such as euphoria. Additionally, areas of the brain that affect concentration, posture, balance, memory, and thinking can also get affected.
The THC in marijuana causes a release of dopamine, which makes you feel good. However, other neurotransmitters contribute to feelings of euphoria, such as serotonin and GABA.
2. Alleviation Of Anxiety
For some people, weed is all they need to reduce their anxiety. Many feel relaxed and mellow and a bit lightheaded after smoking some weed.
These properties contribute to the “chilled out” reputation weed smokers often have. A study from 2017 showed that using marijuana offered them some relief from anxiety and depression.
The calming effect of marijuana is attributed to CBD, a psychoactive compound. A study has shown that marijuana with high CBD and low THC levels caused a 58% reduction in anxiety in a group of people dealing with anxiety and sleep problems.
The effects persisted for a month, meaning marijuana can lower anxiety even when taken in low doses.
However, experts have still not completely understood how CBD works. Still, it is believed to bind to the receptors in the endocannabinoid system, making the body produce its stress-reducing cannabinoids.
Weed increases the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that lowers anxiety. Studies have shown that CBD may have effects similar to those of serotonin, which is the hormone that regulates mood, sleep, and other functions in the body.
3. Exacerbating Anxiety

While marijuana can help many people feel “chilled out,” it can also make anxiety worse. This happens when the drug slows down some brain functions.
In some people, marijuana can result in panic, paranoia, anxiety, and even psychosis.
High levels of THC are often associated with anxiety.
This marijuana property is known as a “biphasic effect,” whereby weed can cause relief in small doses and increase stress in larger quantities.
Some of the people who smoked weed with high doses of THC ended up suffering from psychosis.
Experts think that fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) deactivates anandamide. This means people with a genetic predisposition to producing reduced amounts of this enzyme are more likely to suffer from anxiety when consuming large doses of THC.
4. Enhanced Creativity

For ages, weed has been described as having the ability to get creative juices flowing. This reputation has been growing over time, with many artists saying that weed made them more creative.
According to research, these people might be telling the truth as weed has been found to make creative people see more possibilities. Marijuana can affect our perceptions of reality and enable us to see things uniquely.
During this process, the brain can come up with unique ideas. This is known as the “psychotomimetic effect.”
Based on neuroimaging studies, weed makes cerebral blood flow to the frontal lobe, the amygdala, and the nucleus accumbens. These brain parts are associated with new ways of thinking, which is why they are also linked to creativity.
This kind of thinking focuses on solutions and is often spontaneous. However, the dose of marijuana consumed also matters.
In general, low doses of marijuana enhance creativity, while higher doses hinder creativity.
However, experts also wonder if naturally creative people are more likely to use weed, which means its association with creativity might not have much to do with enhancing this trait.
5. Increased Heart Rate

An increase in heart rate is part of the reason people feel anxious after smoking some weed. As it turns out, the heart rate can go up within two to three minutes of smoking marijuana.
Typically, the heart rate can increase by between 20 to 50 beats above its average rapidity.
This happens because THC gets into the blood quickly, reaches the brain, and activates CB1 receptors. That is why many people feel an almost immediate high after inhaling marijuana smoke.
The blood vessels vasodilate and cause a decrease in blood pressure, which means the heart has to beat a little faster to pump blood throughout the body. Experts believe that the heart has to work 30% faster to reduce blood pressure.
However, there is no conclusive evidence that marijuana has a negative impact on cardiovascular health. While some studies have shown that the risk of heart attack increases after taking marijuana, other studies suggest that this drug can have a therapeutic effect on the heart.
What is more likely is that the dosage determines what effect weed will have on the heart.
6. Bloodshot Eyes

One of the ways people can tell you have smoked marijuana is by looking at your eyes. Marijuana smoking often leads to red, bloodshot eyes.
Initially, it was assumed the smoke got into the eyes and irritated them, appearing red.
However, scientists now understand that the eyes turn red due to vasodilation. When the blood vessels in the body expand, blood pressure goes down, and more blood flows into the eyes, making them look red and glassy.
This reduction in blood pressure is also the reason some weed smokers feel dizzy after taking this drug.
Surprisingly, this effect on the eyes is a good thing as it makes weed a potential remedy for glaucoma, resulting in damaged optic nerves and blindness. However, studies show that CBD can make glaucoma worse by increasing the amount of pressure in the eye.
Finally, it is possible for the eyes to react to the marijuana smoke and turn red.
7. Pain Relief

The “indica” strain of marijuana has been linked to pain relief due to its ability to sedate, relax, and induce sleep. The “Sativa” strain, by contrast, acts as a stimulant.
However, experts don’t think the differences between the two strains are so clear-cut.
It is estimated that more than 50% of young Americans have tried using weed at some point in their lives. Apparently, medical marijuana is often used by people who are trying to manage their pain.
Generally, some strains of marijuana are claimed to be more effective at relieving pain than their counterparts.
Marijuana lowers pain with the help of THC, which triggers CB1 and CB2 receptors. The CBD found in marijuana is also believed to have notable capabilities as an analgesic.
8. Reduced Inflammation

Through its anti-inflammation properties, weed contributes to pain relief. This critical health benefit is achieved when THC activates CB1 receptors in the central nervous system.
More importantly, THC activates CB2 receptors on immune cells, and the result is usually reduced levels of pain to the inflamed tissue.
Additionally, caryophyllene, a terpene present in marijuana, can activate CB2 receptors and lower inflammation. In turn, this results in reduced feelings of pain.
Caryophyllene is a non-cannabinoid compound, and it is found in greater quantities in certain Indica marijuana strains. It has proved effective at dealing with various forms of inflammation in chronic illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease.
The CBD in weed is also known to lower the production of cytokines. These are chemical messengers in the body that generate inflammation as a way to counter infections and viruses.
For this reason, scientists think that CBD may be helpful when dealing with conditions that cause chronic pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, mainly when used together with antirheumatic medications.
9. Heightened Senses

Although smoking weed is associated with side effects like relaxation and pain relief, it can also give some users a heightened sense of smell, sight, and other sensations. For some people, colors might be more vibrant after smoking weed, and sounds might feel more intrusive and noticeable.
For others, there might be an increased sensitivity to particular smells. Some people get visual or auditory hallucinations, which might have something to do with the increased creativity some people get after smoking weed.
Researchers believe THC is responsible for this increase in sensations, which binds to receptors and causes an increase in sensory perceptions, and improves certain forms of awareness and appreciation.
Smoking weed has also been linked to an increase in appetite, informally known as “the munchies.”
Experts think THC makes the olfactory bulb in the body boost a sense of smell and taste, which increases appetite.
Some experts think THC increases the amount of ghrelin, or the “hunger hormone,” which would result in increased appetite.
10. A Feeling Of “Oneness”

Smoking weed can have psychedelic effects, especially after using strains that have high amounts of THC. That means consuming the drug can alter consciousness as LSD does.
In particular, some people feel a sense of “oneness” with nature after smoking weed. Some psychologists call this “oceanic boundlessness.”
This feeling makes people feel “at one” with their surroundings and feel that everything around them is incredible. These feelings can be therapeutic.
They can also result in improved mental health.
11. Marijuana Dependency

It is possible for recreational marijuana use to turn into an addiction. However, in most cases, this doesn’t happen.
That said, marijuana’s ability to cause an addiction should not be taken lightly. Estimates indicate that about 30% of people end up having problems with marijuana use.
This group experiences withdrawal symptoms after they stop smoking weed. These symptoms include mood and sleep problems, irritability, restlessness, cravings, and even loss of appetite.
Smoking weed gives your body a specific dose of THC, which stimulates the reward pathway in the brain and fires up dopamine, which results in feelings of pleasure. So, the body can easily associate smoking weed with satisfaction and learn to motivate you to keep doing it.
According to research, heavy marijuana use can affect the dopamine system and result in a reduced response to dopamine. So, the drug can feel less pleasurable as time goes by, making you smoke more regularly to achieve the same feeling the drug gave you when you first used it.
12. Dry Mouth

One of the effects of smoking marijuana is experiencing a cottonmouth. This means having a dry mouth, tongue, or throat.
Scientifically, the effect is known as xerostomia, and a lack of saliva causes it.
Marijuana causes this undesirable side effect when THC binds to endocannabinoid receptors found in the submandibular glands in the mouth. This blocks the production of saliva for some time.
Before the THC attaches itself to these receptors, it goes throughout the body. That means that whether you smoke or consume marijuana through edibles, this effect is unavoidable.
However, it is not that marijuana makes you dehydrated. It is just that it makes the salivary glands shut down.
13. Distorted Perception Of Time

As you know by now, marijuana can alter your perception of reality, and that includes your ability to perceive time, an effect known as “time dilation.”
So, a minute can feel like two when you are high on weed.
However, some people have been known to overestimate time while others underestimate it after getting high on weed.
This time dilation effect is more powerful in people who take weed by smoking it. That is because smoking weed gets it into the body a lot faster.
Additionally, regular weed smokers don’t have this problem as often as newbies. It is not clear how this effect comes about.
However, experts think THC acts on the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain area that determines time perception, altering its regular operation.
14. Higher Libido

More research is necessary to establish how marijuana affects libido. However, some people experience a greater sex drive after consuming this drug.
Studies have even linked weed users to more sex than non-users.
Among women, the drug has also been linked to greater sex drive and greater satisfaction with orgasms.
Experts think this has something to do with the drug affecting the brain area that regulates sex hormones. THC is also thought to affect testosterone levels.
These effects enhance sexual function in many ways. Weed is also thought to lower sexual inhibitions and prolong pleasurable sensations, which might result in an increased ability to experiment.
That is why some men call weed a “natural viagra,” as it results in increased sexual stamina. However, experts think that these men might be experiencing a distorted time perception, making them feel that sex is taking longer.
That said, scientists have also shown that stimulation of CB1 receptors can delay ejaculation, which might result in sex lasting longer.
15. Lower Libido

It turns out that not everyone can enjoy the sex-enhancing benefits of smoking weed. Instead of experiencing the aphrodisiac effects of weed, some people report lower sexual performance.
Marijuana can cause erectile dysfunction, which a study found to be twice as high in weed users as opposed to non-users.
A study established that weed binds to receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, which is known to have a regular erectile function in males.
Additionally, marijuana’s ability to delay ejaculation can also negatively affect sexual function, with men who smoked weed daily claiming that they had a problem reaching orgasm.
For a while, smoking marijuana has also been thought to result in poor sperm quality. A study from 2015 showed that men who smoked more than once a week had a 29% lower sperm count than men who smoked once a week or less.
Interestingly, another study found out that men who had smoked weed at some point in their lives had higher sperm counts than those who never smoked at all. Based on this finding, it is believed that moderate marijuana use can actually improve reproductive health in men.
16. Increased Forgetfulness
For decades, stoners have had a reputation for being incredibly forgetful. Today, there is some evidence that smoking weed can have a negative effect on memory.
Evidence even suggests that weed may harm a teenager’s brain more than alcohol ever could. This means marijuana has the ability to alter the neural tissue in the brain.
More specifically, marijuana has been linked to reduced thinking ability and compromised short-term memory. The drug can also affect psychomotor function or activities that need attention and coordination.
THC binds to receptors that affect memory formation, and this results in weaker connections between neurons.
Ironically, other studies have shown that weed can prevent and even slow down dementia and neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s through CBD’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
However, more research is necessary to determine to what extent marijuana effects or improves various brain functions. It is believed that the adverse effects marijuana has on the brain are often temporary and reversible even after years of marijuana use.
JOSHUA PUBLISHED IN OCT 2021 / UPDATED IN NOV 2021 (Thoughtvova)

